IGCSE Maths: Mastering Percentages, Reverse Percentages, and Compound Interest (H)
Percentages are arguably the most frequently used mathematical concept in everyday life, finance, and economics. In the Edexcel IGCSE 4MA1 Higher Tier syllabus, the demands extend far beyond basic calculations. Students aiming for Grades 7-9 must master the application of percentages to complex scenarios, including reverse percentages and compound growth and decay.
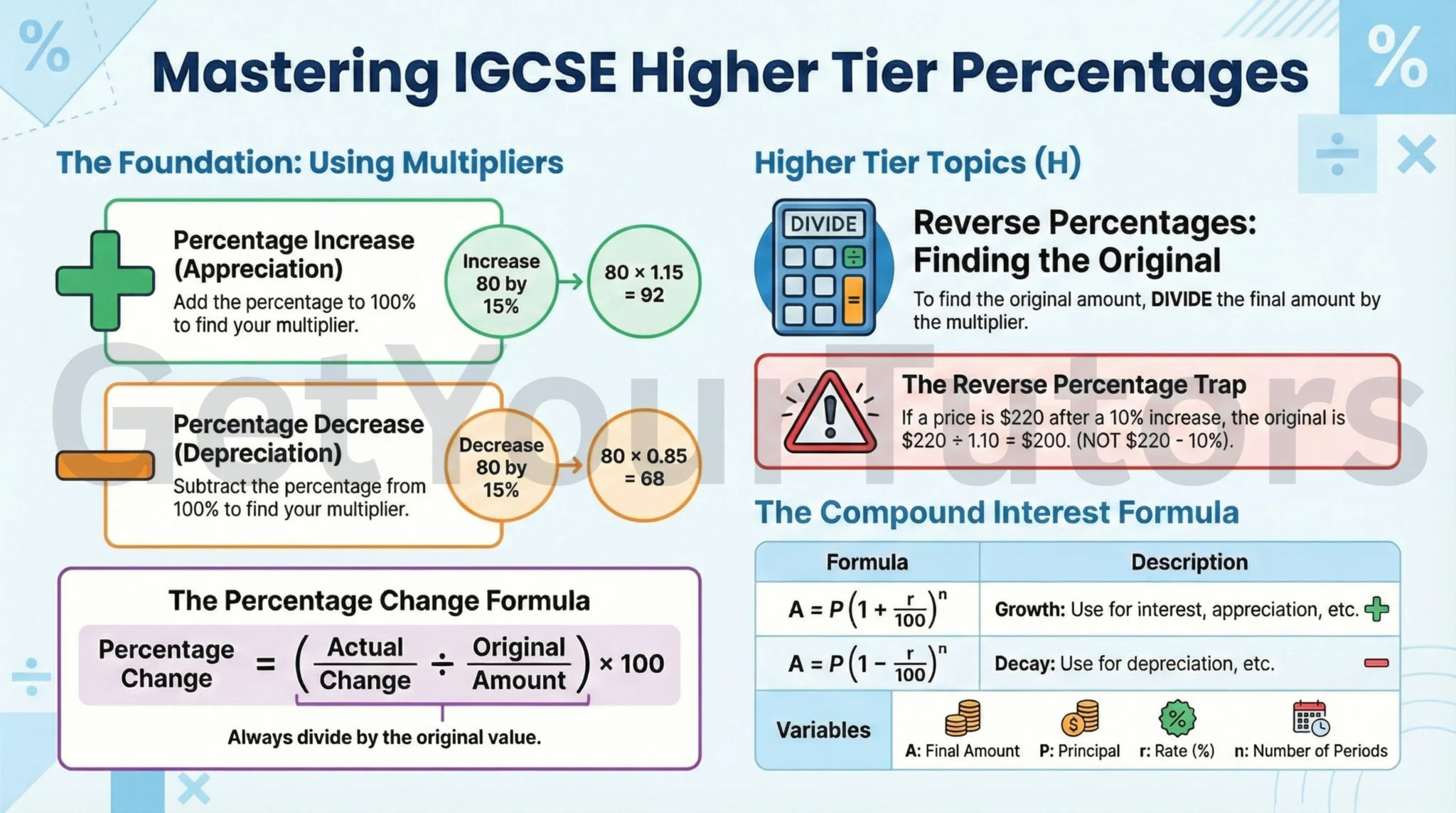
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of Topic 1.7 within the IGCSE Number System, focusing on the efficient use of multipliers and the advanced techniques required for the Higher Tier exam.
The Foundation: The Power of Multipliers
"Percent" means "out of one hundred." Fluency in converting between Fractions, Decimals, and Percentages (FDP) is essential.
The Multiplier Method
The most efficient and robust way to handle percentage calculations in the IGCSE exam is by using decimal multipliers.
1. Finding a Percentage of an Amount:
Convert the percentage to a decimal (divide by 100) and multiply.
Example: Find 15% of 80.
Multiplier = 0.15. Calculation: 0.15 × 80 = 12.
2. Percentage Increase (Appreciation):
Start with 100% (the original amount, multiplier = 1). Add the percentage increase.
Example: Increase 80 by 15%.
Multiplier = 100% + 15% = 115% = 1.15.
Calculation: 1.15 × 80 = 92.
3. Percentage Decrease (Depreciation):
Start with 100% (multiplier = 1). Subtract the percentage decrease.
Example: Decrease 80 by 15%.
Multiplier = 100% - 15% = 85% = 0.85.
Calculation: 0.85 × 80 = 68.
Percentage Change (Profit and Loss)
Percentage change measures the relative difference between a new value and an original value. This is often used in contexts of profit, loss, or error.
Formula for Percentage Change:
Key Strategy: The denominator must always be the original value (the value before the change).
Example: Calculating Profit
Question: A shop buys a product for $50 and sells it for $65. Calculate the percentage profit.
Solution:
Actual Profit = $65 - $50 = $15.
Original Amount (Cost Price) = $50.
Percentage Profit = 1550 × 100 = 0.30 × 100 = 30%.
Reverse Percentages (H)
Reverse percentages involve finding the original amount before a percentage change occurred. This is a crucial Higher Tier concept.
The Concept
If an amount has been increased by 10%, the new amount represents 110% of the original. To find the original amount, you must divide by the multiplier (1.10), not subtract 10% from the new amount.
The Methodology
- Identify the percentage the final amount represents (e.g., 115% if increased by 15%, or 85% if decreased by 15%).
- Determine the corresponding decimal multiplier.
- Divide the final amount by this multiplier to find the original amount.
Formula:
Example: Reverse Percentage Decrease
Question: A car depreciated by 20% and is now worth $12,000. What was its original value?
Solution:
- Percentage Remaining: 100% - 20% = 80%.
- Multiplier: 0.80.
- Calculation: Original Value = 12000 ÷ 0.80 = 15000.
Answer: $15,000.
Compound Interest, Growth, and Decay (H)
Compound interest (or compound growth/decay) occurs when the percentage change is applied repeatedly over time, and the change is calculated on the new amount each period. This leads to exponential functions.
The Compound Interest Formula
This formula is essential and relies on understanding the Laws of Indices.
Where:
- A = Final Amount (Future Value)
- P = Principal Amount (Initial Value)
- r = Interest rate per period (as a percentage)
- n = Number of periods (e.g., years)
The term (1 + r100) is simply the multiplier for the growth rate.
For Compound Decay (Depreciation):
Step-by-Step Worked Examples
Example 1: Complex Percentage Change (Grade 7)
Question: In 2023, a company's revenue was $500,000. In 2024, the revenue increased by 15%. In 2025, the revenue decreased by 5% compared to 2024. What was the revenue in 2025?
Solution:
- Calculate 2024 Revenue (Increase):
Multiplier = 1 + 0.15 = 1.15.
2024 Revenue = $500,000 × 1.15 = $575,000 (M1). - Calculate 2025 Revenue (Decrease from 2024):
Multiplier = 1 - 0.05 = 0.95.
2025 Revenue = $575,000 × 0.95 = $546,250 (A1).
Note: This can be done in one step: $500,000 × 1.15 × 0.95.
Example 2: Reverse Percentage (Non-Calculator Method) (Grade 8)
Question: A price is increased by 12.5%. The new price is $270. Find the original price.
Solution:
- Identify Percentage: 100% + 12.5% = 112.5%.
- Determine Multiplier: 1.125 (M1).
- Divide: Original Price = $270 ÷ 1.125.
(Non-calculator method: Recognize 12.5% = 1/8. So 112.5% = 1 + 1/8 = 9/8).
Original Price = $270 ÷ 98
$270 × 89 = (270 ÷ 9) × 8 = 30 × 8 = 240. - Result: $240 (A1).
Example 3: Compound Interest Calculation (Grade 8)
Question: $5000 is invested at a compound interest rate of 3% per annum for 4 years. Calculate the total value of the investment after 4 years.
Solution:
- Identify Variables: P=5000, r=3, n=4.
- Determine Multiplier: 1 + 3100 = 1.03.
- Apply Formula (M1):
A = 5000 × (1.03)4. - Calculate:
A = 5000 × 1.12550881...
A = 5627.54405... - Round (Money requires 2 decimal places):
$5627.54 (A1).
Example 4: Compound Decay with Changing Rates (Grade 9)
Question: A new car costs $20,000. It depreciates by 15% in the first year, and 10% per year thereafter. What is its value after 3 years?
Methodology: This is a multi-step compound decay problem with changing rates. We apply the multipliers sequentially.
Solution:
- Year 1 Depreciation (15%):
Multiplier = 0.85. - Year 2 and 3 Depreciation (10%):
Multiplier = 0.90. This is applied twice. - Calculation (M2):
Value after Year 3 = $20,000 × 0.85 × 0.90 × 0.90
Value = $20,000 × 0.85 × (0.90)2
Value = $20,000 × 0.6885 = $13,770.
Answer: $13,770 (A1).
Example 5: Finding the Rate (Grade 9)
Question: $10,000 is invested for 5 years at a compound interest rate of r% per annum. After 5 years, the investment is worth $12,166.53. Calculate the value of r.
Methodology: Use the compound interest formula and solve for r. This requires taking the nth root.
Solution:
- Set up the equation (M1):
12166.53 = 10000 × (1 + r100)5. - Isolate the multiplier term:
12166.5310000 = (1 + r100)5.
1.216653 = (1 + r100)5. - Take the 5th root (M1):
5√1.216653 = 1 + r100.
1.040000... ≈ 1 + r100. - Solve for r:
0.04 = r100.
r = 4 (A1).
Real-World Application (Global Context)
Percentages are fundamental to understanding global economic indicators, such as inflation rates and real wage growth.
Scenario: Calculating Real Wage Growth
An employee receives a nominal wage increase, but inflation must be accounted for to determine the real change in purchasing power.
Problem: An employee's salary increased from $60,000 to $62,400 in one year. During the same period, the inflation rate was 3.5%. Calculate the percentage change in the employee's real wage.
Solution:
- Calculate the Nominal Wage Increase:
Change = $62,400 - $60,000 = $2,400.
Nominal Increase = 240060000 × 100 = 4%. - Analyze the Real Wage Change:
The employee received a 4% increase (Multiplier 1.04), but prices rose by 3.5% (Multiplier 1.035). - Calculate Real Wage Growth (Precise Method):
Real Growth Multiplier = Nominal Multiplier ÷ Inflation Multiplier
Real Growth Multiplier = 1.04 ÷ 1.035 ≈ 1.00483.
This is a 0.483% increase.
(An approximation method, often sufficient, is Real Growth ≈ Nominal Growth - Inflation Rate = 4% - 3.5% = 0.5%.)
Answer: The employee's real wage increased by approximately 0.48% (or 0.5% using the approximation).
Exam Technique and Common Pitfalls
Percentage questions often look simple but contain traps that cost students crucial marks.
The Reverse Percentage Trap
The single biggest error in this topic is incorrectly applying a percentage change to find the original amount.
- Scenario: Price increased by 10% to $220.
- Error: Calculating 10% of $220 ($22) and subtracting it ($220 - $22 = $198).
- Fix: Realizing that $220 represents 110% (1.10). The correct method is $220 ÷ 1.10 = $200.
Compound Interest vs. Simple Interest
Ensure you read the question carefully.
- Simple Interest: Interest is only calculated on the principal. Total Interest = P × r100 × n.
- Compound Interest: Use the formula A = P(1 + r100)n. IGCSE Higher Tier questions predominantly feature compound interest.
Rounding Errors in Multi-Step Problems
When dealing with multi-year compound interest problems, do not round intermediate results. Use the full calculator display or the 'Ans' button. Round only the final answer (usually to 2 decimal places for currency). Premature rounding can lead to losing the final accuracy mark (A1).
It is vital to master these high-value exam topics as they are tested frequently and often involve multiple steps.
Summary Checklist and Next Steps
Fluency with percentages, especially the Higher Tier applications, is essential for achieving a top grade in the IGCSE exam.
Checklist:
- [ ] I can efficiently use decimal multipliers for percentage increase and decrease.
- [ ] I can calculate percentage change (Profit/Loss) using the correct formula, always dividing by the original amount.
- [ ] (H) I can identify and correctly solve reverse percentage problems by dividing by the multiplier.
- [ ] (H) I can apply the compound interest/growth/decay formula accurately.
- [ ] (H) I can solve complex problems involving changing rates or finding the rate/time (Grade 9).
Practice Resources
Mastering percentages, especially reverse percentages and compound interest, requires practice. Use our dedicated worksheet to test your skills on these high-tariff exam topics.
Download Topic Worksheet: Percentages, Reverse & Compound Interest
Looking for more practice? Access our complete library of IGCSE maths worksheets and answers:
Get Free IGCSE Edexcel Maths Worksheets & Answers
Next Steps:
The natural progression from percentages is Topic 1.8: Ratio and Proportion. Understanding how quantities relate to each other through ratios builds upon the comparison skills developed in this section.