IB Math AI HL vs. SL: Is HL Worth the Effort for Non-STEM Students? (Dubai Guide)
In today’s increasingly data-driven world, mathematical literacy, specifically the ability to analyze data and utilize mathematical modeling is no longer confined to traditional STEM fields. Disciplines such as Business, Finance, Economics, Psychology, and Data Science demand strong quantitative skills.
The International Baccalaureate (IB) responded to this demand by introducing the Mathematics: Applications and Interpretation (AI) stream. It is designed to equip students with the practical mathematical tools needed for the modern workplace.
However, for ambitious students in Dubai choosing their Diploma Programme (DP) courses, a significant dilemma arises: Is the Standard Level (SL) sufficient, or does the Higher Level (HL) provide a significant advantage, justifying the extra effort?
The gap between AI HL and SL is significant, involving substantial differences in content, pace, and technological demands. Contrary to some misconceptions, AI HL is a rigorous course that offers substantial value for ambitious students heading into quantitative non-STEM fields.
Executive Summary: Key Takeaways
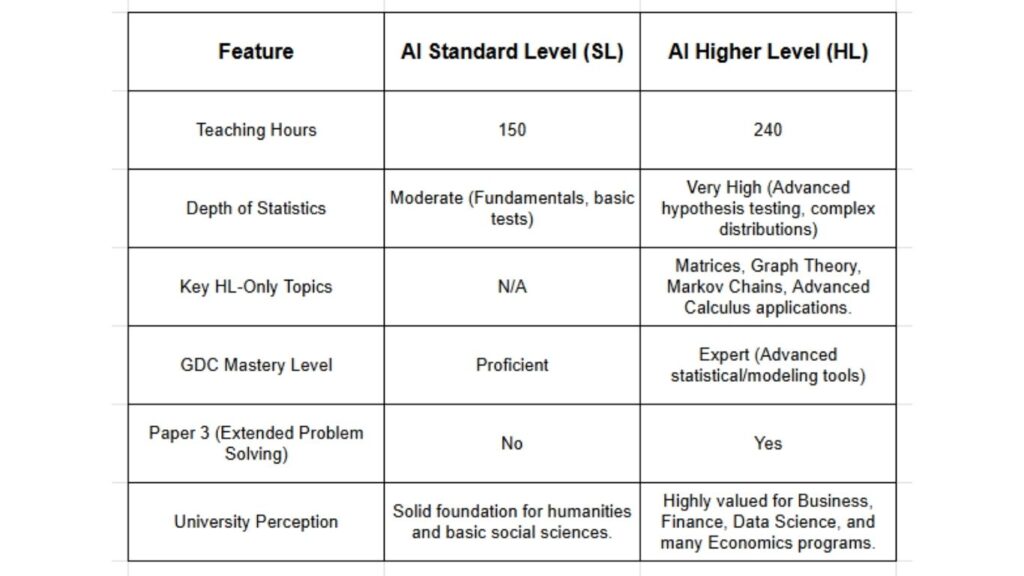
Significant Difficulty Gap: AI HL is considerably more demanding than AI SL, featuring advanced topics, a faster pace (240 vs. 150 hours), and higher expectations for interpretation and modeling.
Advanced Content at HL: HL includes sophisticated topics such as Matrices, Graph Theory, advanced hypothesis testing (e.g., t-tests, chi-squared), and deeper applied calculus.
GDC Mastery is Crucial: Both levels rely heavily on the Graphic Display Calculator (GDC), but AI HL requires expert-level proficiency in advanced statistical packages and modeling tools.
Paper 3 (HL Only): AI HL includes a challenging third examination paper focused on extended problem-solving and investigation.
Value Proposition for Non-STEM: AI HL is highly valued for competitive Business, Finance, Data Science, and many Economics programs globally, providing a significant advantage over SL.
Debunking the Myth: AI HL is a rigorous mathematical course, not an “easy HL option.”
The AI Philosophy: Modeling, Statistics, and Technology
The Applications and Interpretation (AI) stream emphasizes the practical application of mathematics. Its philosophy is rooted in using mathematical models, statistical analysis, and technology (the GDC) to solve real-world problems. It focuses less on abstract theory and proof, and more on interpretation and justification of results in context.
This guide focuses specifically on the Applications and Interpretation (AI) stream. If you are considering pathways requiring pure mathematics or theoretical rigor, such as Engineering or Physics, you should review the Analysis and Approaches (AA) stream detailed in our definitive guide comparing IB Math AA vs. AI.
The Syllabus Divide: Where AI HL and SL Diverge
While AI SL provides a solid foundation in applied mathematics, AI HL delves significantly deeper into sophisticated techniques relevant to university-level studies in quantitative fields.
1. Statistics and Probability (The Biggest Gap)
This is where the divergence is most pronounced. AI SL covers fundamental statistics and distributions. AI HL expands this significantly to include:
Advanced Hypothesis Testing: Conducting and interpreting tests like the t-test, chi-squared tests (goodness of fit and independence).
Confidence Intervals: Calculating and interpreting confidence intervals for various distributions.
Distributions: Deeper exploration of distributions, including the Poisson distribution.
Bivariate Statistics: More complex regression analysis and understanding correlation.
These statistical tools are the backbone of research in social sciences, economics, and business analytics.
2. Modeling and Functions
AI SL focuses on using standard functions (linear, quadratic, exponential) to model data. AI HL introduces sophisticated mathematical structures and techniques:
Matrices and Markov Chains: Using matrices for transformations and modeling dynamic systems (e.g., population movement, financial markets).
Graph Theory: Exploring networks, adjacency matrices, and algorithms (e.g., finding the shortest path or analyzing connectivity). This is highly relevant to logistics, computer science, and social network analysis.
Complex Modeling: Developing and critically evaluating sophisticated models for real-world scenarios.
3. Applied Calculus
Both levels cover calculus, but the emphasis is on application rather than theoretical proof. HL goes deeper into:
Optimization: Solving complex optimization problems using calculus and technology.
Kinematics: Analyzing motion in greater depth.
Volumes of Revolution: Calculating volumes of complex shapes.
Differential Equations: Introduction to modeling with differential equations (e.g., logistic growth).
Beyond the Syllabus: Pace, Rigor, and Technology
The experience of studying AI HL is fundamentally more intense than AI SL.
Pace and Hours: The IB mandates 240 teaching hours for HL and 150 hours for SL. This structural difference means AI HL covers significantly more content at a much faster pace. The workload and independent study required for HL are substantially higher.
Rigor of Interpretation: The rigor of AI HL lies not in abstract proof (like AA HL), but in the sophistication of interpretation. HL students must critically evaluate the limitations of their mathematical models, justify their choice of techniques (e.g., choosing the correct statistical test), and communicate their findings with precision within a real-world context. This requires strong critical thinking skills.
The GDC Factor: A Higher Level of Mastery
The Graphic Display Calculator (GDC, such as the TI-Nspire) is essential for all AI courses, as there is no non-calculator paper. However, the level of mastery required for AI HL is significantly higher.
AI HL students must be expert users, proficient in:
Advanced Statistical Packages: Running complex hypothesis tests and analyzing distributions efficiently.
Matrix Operations: Performing calculations and solving systems using matrices.
Complex Modeling Tools: Utilizing dynamic graphing and spreadsheet functions to model and solve problems.
In the exam, time wasted struggling with the GDC will severely impact performance.
The Assessment Differences: Papers 1, 2, and the Investigative Paper 3
The examination structure also reflects the increased demands of the HL course.
Papers 1 and 2 (GDC Required)
Both SL and HL students sit Paper 1 (short-response questions) and Paper 2 (extended-response questions). However, the HL papers are longer and feature significantly more complex, unstructured problems. HL questions often require students to develop their own models rather than applying a standard technique.
The Crucial Difference: Paper 3 (HL Only)
This is a defining feature of AI HL. Paper 3 is a 1-hour exam consisting of two extended, compulsory problem-solving questions.
Paper 3 is challenging because it often involves significant data analysis, complex modeling, or investigation into an unfamiliar scenario. It tests the student’s ability to synthesize knowledge, utilize technology effectively, and interpret results under pressure.
The Internal Assessment (IA) at HL vs. SL
The Internal Assessment (IA) accounts for 20% of the final grade at both levels, using the same criteria. However, the expectations for mathematical sophistication are higher at HL.
An HL IA must involve mathematics “commensurate with the level of the course.” This means HL students are expected to utilize the advanced techniques learned in the HL syllabus (e.g., sophisticated statistical tests, matrix models) and demonstrate a deeper level of reflection and analysis than SL students.
The Internal Assessment (IA) is an ideal opportunity for AI students to apply their skills to real-world data. At HL, students must demonstrate a level of sophistication commensurate with the course. Selecting an appropriate statistical method and executing the analysis rigorously is crucial, as detailed in our comprehensive guide to the IB Math IA.
The Comparison Matrix
University Admissions: The Advantage of AI HL
For students targeting competitive non-STEM pathways, AI HL offers a significant advantage over AI SL, demonstrating quantitative rigor and relevant skills.
Business, Finance, and Management
AI HL is excellent preparation for these fields. The focus on financial modeling, statistics, and optimization is directly applicable to university business courses. Top business schools view AI HL favorably as it demonstrates strong quantitative skills in a practical context.
Economics
The choice for Economics is nuanced. Top-tier, highly quantitative programs (e.g., LSE, Oxbridge, elite US programs) still mandate AA HL due to its theoretical rigor. However, AI HL is increasingly accepted and valued by many strong Economics programs globally. Its focus on statistics and modeling is highly relevant to modern economic analysis.
Data Science and Analytics
AI HL is arguably the best foundation available at the high school level for this rapidly growing field. The rigorous training in statistics, modeling, and technology provides a direct pathway into university-level data science
Social Sciences (Psychology, Sociology)
For students pursuing social sciences, the statistical rigor of AI HL provides a strong advantage, equipping them with the tools necessary for quantitative research methods at the university level.
The UK Context: While recognition of AI HL is growing, UK university policies remain complex and varied, especially for Economics and competitive Business programs. Students targeting the UK must carefully review our detailed analysis of UK university math requirements to ensure their choice aligns with prerequisites.
Choosing Your Level: A Framework for Decision Making
Deciding between AI HL and SL requires balancing university goals with a realistic assessment of abilities and workload.
Assessing Readiness for AI HL: Strong candidates for AI HL possess:
A genuine interest in statistics and real-world modeling.
Strong proficiency and comfort with technology (GDC).
Good critical thinking and interpretation skills.
A solid foundation in MYP Extended Mathematics (or equivalent).
The Workload Consideration: AI HL is demanding. Students must balance this workload with their other DP subjects. The goal is to maximize the total IB score.
The “Better Grade” Rule: If AI HL is not explicitly required or strongly preferred for your university pathway, a ‘7’ in AI SL is generally viewed more favorably than a ‘4’ or ‘5’ in AI HL.
IB Math AI HL is a rigorous, demanding course that requires strong technological skills and the ability to interpret complex models. The pace is fast, and the expectations for Paper 3 and the IA are high. Students aiming for top marks often benefit from specialized IB Math AI HL tutoring to master the advanced statistical techniques and GDC functionalities required.
Conclusion: The Modern Math Pathway
IB Math AI HL represents a modern approach to mathematics education, prioritizing skills essential for the 21st century. It is a challenging and valuable pathway for ambitious students heading into data-driven fields. By understanding the significant differences between HL and SL, students in Dubai can make an informed choice that aligns with their strengths and future aspirations.
Choosing between AI HL and AI SL requires careful consideration of your interests, strengths, and future goals. Whether you opt for the rigorous demands of HL or the solid foundation of SL, our team of expert IB math tutors in Dubai specializes in the Applications and Interpretation stream and can help you achieve your full potential.
Frequently Asked Questions
It is significantly harder. AI HL covers much more content (240 hours vs. 150 hours), including advanced topics like Matrices, Graph Theory, and complex statistical testing. HL also requires a higher level of interpretation and includes the challenging Paper 3 examination.
Yes, AI HL is highly respected by top business schools globally. Its focus on statistics, financial modeling, and optimization provides excellent preparation for university-level business and finance courses.
It depends on the university. Highly quantitative Economics programs (especially top-tier UK universities like LSE or Cambridge) typically require AA HL. However, many strong Economics programs worldwide accept and value AI HL due to its relevance to modern economic analysis and statistics. You must check specific university prerequisites.
The main difference is the philosophy and focus. AI HL focuses on applied mathematics: statistics, modeling, technology (GDC), and real-world interpretation. AA HL focuses on pure mathematics: theoretical calculus, abstract reasoning, and rigorous proof, including a non-calculator paper.
Expert-level GDC skills are essential for AI HL. Students must master advanced statistical packages (hypothesis testing, distributions), matrix operations, financial solvers, and complex graphing and modeling tools to model scenarios efficiently and accurately under exam conditions.