IB Math AA (Analysis and Approaches) vs. AI (Applications and Interpretation): The Definitive Guide (Dubai Context)

Selecting courses for the International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme (IB DP) is a pivotal moment for Grade 10/Year 11 students in Dubai. Among these choices, the decision regarding which mathematics pathway to pursue is arguably the most critical and often the most confusing. The implications for university admissions, particularly for competitive STEM, Economics, and Business programs, are significant.
In 2019, the IB overhauled its mathematics curriculum, replacing the old structure with two distinct streams: Analysis and Approaches (AA) and Applications and Interpretation (AI), both offered at Higher Level (HL) and Standard Level (SL).
This guide, informed by years of experience advising students in top-tier UAE international schools, aims to demystify these options. The “right” choice is highly individualized, depending on a student’s mathematical strengths, their genuine interest in the subject, and, most importantly, their future academic and career goals.
Executive Summary: Key Takeaways
Two Distinct Philosophies: AA focuses on theoretical mathematics, analytical rigor, and proof. AI focuses on practical application, modeling, statistics, and the use of technology.
Analysis and Approaches (AA): The essential pathway for students pursuing Mathematics, Engineering, Physics, and highly quantitative Economics. It emphasizes calculus and algebraic fluency.
Applications and Interpretation (AI): The ideal pathway for students interested in Social Sciences, Business, Psychology, Data Science, and certain Life Sciences. It emphasizes statistics and modeling.
The Role of Technology (GDC): AA includes a mandatory non-calculator paper (Paper 1). AI relies heavily on the Graphic Display Calculator (GDC) for all papers.
Debunking the Myth: AI is NOT the old “Math Studies.” AI HL is a rigorous course demanding sophisticated modeling skills and interpretation.
University Requirements are Key: Course selection must be driven by university prerequisites. Top-tier STEM programs globally often mandate AA HL.
The IB's Philosophy and the 2019 Overhaul
Why did the IB create two distinct pathways? The rationale was to acknowledge the diverse ways mathematics is used in the modern world.
Previously, students with different needs were often forced into the same classes. The new structure aims to provide rigorous pathways for both types of students:
The Analytical Path (AA): For students who need deep theoretical understanding and strong analytical tools for STEM.
The Applied Path (AI): For students who need skills in data analysis, modeling, and technology-driven problem-solving for applied sciences and humanities.
Debunking the Myth: AI is Not “Easy Math” A persistent misconception in Dubai schools is that AI is simply a rebranding of the old, less rigorous “Math Studies.” This is categorically false. Math AI, particularly at Higher Level (AI HL), is a demanding course. It covers complex topics such as advanced statistical testing, matrices, graph theory, and sophisticated mathematical modeling, requiring strong critical thinking and interpretation skills.
Curriculum Deep Dives
Mathematics: Analysis and Approaches (AA) – The Path of Pure Mathematics
AA Philosophy and Focus
Analysis and Approaches (AA) is designed for students who genuinely enjoy mathematics and are comfortable with abstract reasoning. It emphasizes the theoretical underpinnings of mathematics, focusing on analytical rigor and proof. It is the pathway that most closely resembles traditional pre-university math.
AA Syllabus Content Highlights
The AA syllabus is heavily focused on algebraic methods and theoretical depth:
Calculus: A major focus, particularly at HL. It covers the theoretical exploration of differentiation and integration, limits, and rigorous proofs.
Advanced Algebra and Functions: Deep exploration of logarithms, exponentials, sequences, series, and the binomial theorem.
Trigonometry: Rigorous study of trigonometric identities and functions.
HL Specifics: Complex numbers, vectors, and advanced calculus techniques are studied in significantly greater depth.
The Role of Technology (GDC) in AA
A crucial distinction of the AA stream is the presence of a Non-Calculator Paper (Paper 1). This demands exceptional algebraic fluency and the ability to manipulate complex expressions manually. While the GDC is used in other papers (Paper 2, and Paper 3 for HL), the reliance on foundational manual skills is high.
AA HL vs. AA SL
The gap between AA SL and AA HL is substantial. AA HL moves at a much faster pace and dives into considerably more complex and abstract topics. AA HL is considered one of the most challenging courses in the entire IB Diploma Programme. [Identify Link Opportunity: IB Math AA HL vs SL Difficulty Guide]
Who Should Choose AA?
AA (typically at HL) is the required or strongly preferred pathway for:
Mathematics
Engineering (all disciplines)
Physics and Physical Sciences
Computer Science (especially theoretical tracks)
Economics (especially at highly quantitative universities)
The rigor of Math AA, particularly at Higher Level, demands exceptional analytical skills and a strong grasp of abstract concepts. Students undertaking this challenging pathway often require expert support for IB Math AA (HL/SL) to master the complex theories and the demanding techniques required for the non-calculator paper.
Mathematics: Applications and Interpretation (AI) – The Path of Practical Application
AI Philosophy and Focus
Applications and Interpretation (AI) is designed for students who want to understand how mathematics is used to model and solve real-world problems. It emphasizes statistics, data analysis, and the strategic use of technology.
AI Syllabus Content Highlights
The AI syllabus focuses on applied mathematics and includes topics not found in AA:
Statistics and Probability: A very strong emphasis, including hypothesis testing, distributions, and regression analysis.
Financial Mathematics: Amortization, loans, and financial modeling.
Modeling: Using technology to model real-world phenomena.
Calculus (Applied Focus): Focuses on the practical application of calculus (e.g., optimization) rather than theoretical proofs.
HL Specifics: Includes topics like Matrices, Graph Theory, and more sophisticated statistical methods.
The Role of Technology (GDC) in AI
The GDC is essential in Math AI. All examination papers in AI assume full access to a GDC. Students must master advanced GDC functions for statistical analysis, modeling, and complex calculations. The challenge lies not just in calculation, but in knowing which technological tool to use and interpreting the results accurately within the context of the problem.
AI HL vs. AI SL
The gap between AI SL and AI HL is also significant. AI HL requires students to tackle complex modeling problems and understand sophisticated statistical techniques. While less abstract than AA HL, it is demanding in its requirement for interpretation and technological proficiency.
Who Should Choose AI?
AI is an excellent choice for students pursuing:
Business and Management
Social Sciences (Psychology, Sociology)
Data Science (AI HL is excellent preparation)
Life Sciences and Biology (where statistics is key)
Humanities
Math AI is heavily reliant on the effective use of the Graphic Display Calculator (GDC) for modeling and statistical analysis. Mastering the technology and interpreting the results in context are crucial skills. We offer specialized guidance for IB Math AI (HL/SL) focusing on GDC proficiency and mathematical modeling.
Head-to-Head Analysis
AA vs. AI: The Key Differences Analyzed
1. Calculus Content and Depth
Both streams cover calculus, but the approach is different. AA delves deeply into the theoretical underpinnings of calculus, emphasizing proof and analytical techniques. AI focuses on the application of calculus to solve real-world problems, often relying on the GDC to perform the calculations.
2. Statistics and Modeling
This is where the streams diverge most significantly. AI has a much stronger focus on statistics, probability distributions, and hypothesis testing than AA. AI emphasizes the development of mathematical models to represent real-world data.
3. Emphasis on Proof and Rigor
AA places a strong emphasis on mathematical proof and rigorous justification of arguments. Students must be comfortable with abstract reasoning. AI focuses more on interpretation, justification of results in context, and evaluating the validity of a model.
The Comparison Matrix
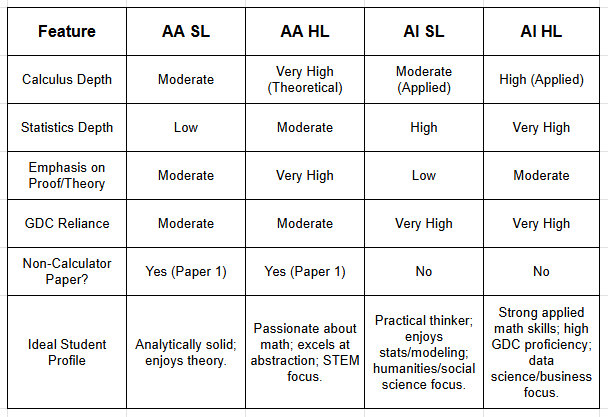
Which Stream is "Harder"?
Neither stream is universally “harder”; they challenge different skill sets.
AA is harder for students who struggle with abstract reasoning, theoretical proofs, and complex algebraic manipulation without a calculator.
AI is harder for students who struggle with interpreting real-world contexts, mastering advanced GDC functions, or understanding the nuances of statistical analysis.
AI HL, in particular, is a challenging course that should not be underestimated.
The Internal Assessment (IA): Differences in Approach
The Internal Assessment (IA), or Mathematical Exploration, accounts for 20% of the final grade in both streams. However, the typical focus differs:
AA IAs often focus on exploring mathematical theories, proofs, or the history of a concept.
AI IAs typically involve statistical analysis of real-world data, developing and testing mathematical models, or applying algorithms.
Regardless of the stream chosen, the Internal Assessment accounts for 20% of the final grade and requires significant independent research and mathematical communication skills. Students should consult our step-by-step guide to structuring the IB Math IA to understand the requirements for achieving top marks.
University Requirements: What Do Universities Prefer?
This is the most crucial factor in the decision-making process. University requirements vary significantly by country and by course. Students in Dubai MUST research the specific requirements of their target universities.
UK (Russell Group/Oxbridge) Requirements
The UK generally has the strictest and most specific requirements, particularly for elite universities.
STEM (Engineering, Physics, Computer Science, Mathematics): Top universities (Oxbridge, Imperial, Russell Group) almost exclusively require or strongly prefer AA HL. AI HL is generally not accepted for these courses.
Economics: Highly quantitative programs (LSE, Cambridge, Oxford, Warwick) mandate AA HL. Other universities may accept AI HL, but AA HL is strongly preferred.
Medicine/Life Sciences: Requirements vary. Some require AA (SL or HL), while others may accept AI HL if accompanied by strong science HLs.
Given the complexity, strictness, and variability of these policies, students applying to the UK must consult our detailed guide to UK university math prerequisites before finalizing their DP choices.
US and Canadian Requirements
North American universities are generally more flexible. They prioritize the rigor of the student’s overall course load (HLs are preferred over SLs).
Elite STEM Programs (MIT, Stanford, Ivy League): AA HL is strongly recommended to demonstrate sufficient mathematical preparation, aligning with the rigor of AP Calculus BC.
General Admissions: Both AA and AI are respected, provided the level (HL/SL) matches the quantitative demands of the major.
European Requirements
Requirements in Europe (e.g., Netherlands, Germany, Switzerland) are highly variable and often country-specific. Many technical universities align with the UK preference for AA HL for STEM programs. Students must research specific country requirements meticulously.
Requirements by Major/Career Path (Summary Table)
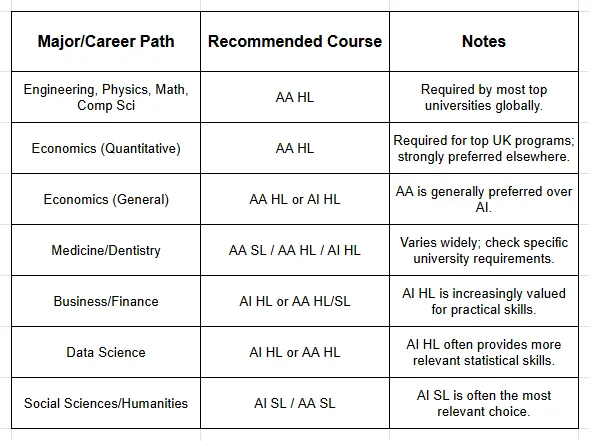
The decision framework should follow this hierarchy:
University Goal (The Deciding Factor): Research the prerequisites for your target courses and universities. If AA HL is required, your decision is made. Do not risk your university application by choosing an unaccepted course.
Mathematical Strength: Be realistic about your abilities. Are you stronger analytically (AA) or in application and technology (AI)? A strong score in SL is better than a weak score in HL.
Interest: Choose the stream that aligns with how you enjoy learning mathematics. Do you prefer theoretical exploration (AA) or practical application (AI)?
Choosing the right IB Mathematics pathway is a critical decision with significant implications for university admissions. If you need personalized guidance on course selection or specialized support in either AA or AI, our team of expert IB math tutors in Dubai can help you navigate this choice and achieve your academic goals.
Frequently Asked Questions
No, they are difficult in different ways. AA is harder if you struggle with abstract theory, proofs, and non-calculator algebra. AI (especially HL) is challenging due to its focus on sophisticated modeling, interpretation of data, and mastery of the GDC. AI SL is generally considered the least demanding of the four options.
You must take IB Math AA HL. This is a requirement for almost all top engineering programs globally, especially in the UK, Canada, and elite US institutions. AI HL is generally not accepted for engineering.
For Economics at top UK universities (e.g., LSE, Oxbridge), AA HL is required. For general Economics programs, AA HL is preferred, though AI HL may be accepted. For Business, AI HL is an excellent choice as the statistical and modeling content is highly relevant, but AA SL/HL is also widely accepted.
It depends on the university and the country. In the UK, requirements vary; some medical schools prefer AA, while others accept AI HL if accompanied by strong HL sciences (Chemistry and Biology). You must check the specific prerequisites of your target institutions.
The GDC is crucial in both, but its role differs. In AI, the GDC is essential for all papers and is used extensively for statistics and modeling. In AA, the GDC is vital for Papers 2 (and 3 at HL), but Paper 1 is non-calculator, requiring strong manual mathematical skills.
It is possible but challenging. While there is some overlap in the core syllabus, the streams diverge quickly. Switching after the first semester of DP1 often requires significant catch-up work. It is much better to make the correct choice before starting the DP.